|
Vikidia currently has 4,621 articles. Improve it! |
|
Join Vikidia: create your account now and improve it! |
Cloud computing
In Computer science, Cloud computing is when the user can simply use storage, computing power, or specially crafted development environments, without having to worry how these work internally. Cloud computing is the development and use of computer technology on the Internet. It rely on the infrastructure of the internet.[1] It is a style of computing in which IT-related capabilities are provided “as a service”,[2] allowing users to access technology-enabled services from the Internet ("in the cloud")[3] without knowledge of, or control over the technologies behind these servers.[4]
Cloud Computing is the way in which information is permanently stored in servers on the Internet and cached temporarily on clients that include computers, laptops, etc.
Cloud computing utilizes software as a service (SaaS), such as Web 2.0 and other technology trends, all of which depend on the Internet for satisfying users' needs. For example, Google Apps provides common business applications online that are accessed from a web browser, while the software and data are stored on the Internet servers.
Brief[edit | edit source]
Comparisons[edit | edit source]
Cloud computing is often confused with grid computing whereby a "super and virtual computer" is composed of a cluster of networked, working together to perform very large tasks.
However many cloud computing deployments are today powered by grids.
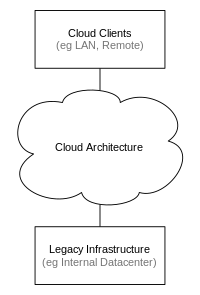
Architecture[edit | edit source]
The majority of cloud computing infrastructure currently consists of reliable services delivered through data centers that are built on computer and storage virtualization technologies. The services are accessible anywhere in the world, with The Cloud appearing as a single point of access for all the computing needs of consumers.
Characteristics[edit | edit source]
As customers generally do not own the infrastructure or know all details about it, mainly they are accessing or renting, so they can consume resources as a service. By sharing consumable and "intangible" computing power between multiple "tenants", utilization rates can be improved (as servers are not left idle) which can reduce costs significantly while increasing the speed of application development. It has been enabled by increased high-speed bandwidth which makes it possible to receive the same response times from centralized infrastructure at other sites.
Providers[edit | edit source]
Cloud computing is being driven by providers including Google, Amazon.com, and Yahoo! as well as traditional vendors including IBM, Intel,[5] Microsoft[6] and SAP.[7] It is adopted from individual users through large enterprises.
History[edit | edit source]
The Cloud[8] is a metaphor for the Internet,[9] or more generally components and services which are managed by others.
In 1960 when John McCarthy expressed his opinion that "computation may someday be organized as a public utility"The word Cloud was already in commercial use in the early 1990s to refer to large Automated teller machine networks.[10] By the turn of the 21st century, cloud computing solutions had started to appear on the market,[11] though most of the focus at this time was on Software as a service.
Amazon.com developed the use of cloud computing when upgrading their data centers after the dot-com bubble and providing access to their systems by way of Amazon Web Services in 2002 on a utility computing basis.
The activity increased in 2007, with Google, IBM and a number of universities starting large scale cloud computing research project,[12] around the time the term started gaining popularity. It was a hot topic by mid-2008.
Political issues[edit | edit source]
Clouds may be used across many countries. As such it raises some issues, whereby providers must satisfy legal restrictions in order to deliver service to a global market.
Although there have been efforts to match the legal environment, providers are currently dealing with international markets (typically the United States and European Union) by deploying local infrastructure and allowing customers to select their countries.[13] However it raises concerns about security and privacy from individual through governmental level.
Architecture[edit | edit source]
Cloud architecture[14] is the systems architecture of the software systems involved in the delivery of cloud computing (eg hardware, software). It typically involves multiple cloud components communicating with each other.
The resulting systems may be more manageable than their "monolithic" counterparts.
Cloud architecture extends to the client where web browsers and/or software applications are used to access cloud applications.
Cloud storage architecture is loosely coupled where metadata operations are centralized enabling the data nodes to scale into the hundreds, each independently delivering data to applications or users.
Key characteristics[edit | edit source]
- location independencethe users are enabled to access systems regardless of location or what device they are using;
- Centralization of infrastructure;
- higher Peak-load capacity
- improvements of utilization, performance and efficiency;
- reliability by way of multiple redundant sites;
Components[edit | edit source]
Application[edit | edit source]
A cloud application influences The Cloud model of software architecture, often eliminating the need to install and run the application on the customer's own computer, thus reducing software maintenance, ongoing operations, and support.
Client[edit | edit source]
A cloud client is computer hardware and/or computer software which relies on The Cloud for application delivery.
It may be a computer, mobile computing (Android, iPhone, Windows Mobile).
Platform[edit | edit source]
A cloud platform is a set of applications using the cloud computing, therefor without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the hardware and software layers.
Service[edit | edit source]
A cloud service (e.g. Web Service) is "software system[s] designed to supportmachine to Machine interaction over a computer network"[15] For example:
- Identity (OAuth, OpenID)
- Integration (Amazon Simple Queue Service)
- Mapping (Google Maps, Yahoo! Maps)
- Payments (Amazon Flexible Payments Service, Google Checkout, PayPal)
- Search (Alexa, Google Custom Search, Yahoo! BOSS)
- Others (Amazon Mechanical Turk)
Storage[edit | edit source]
Cloud storage is the delivery of data storage. For example:
- Database (Amazon SimpleDB, Google App Engine's BigTable datastore)
- Network attached storage (MobileMe iDisk component, Nirvanix CloudNAS)
- Synchronisation (Live Mesh Live Desktop component, MobileMe Push technology functions)
- Web service (Amazon Simple Storage Service, Nirvanix SDN)
Traditional storage vendors may offer their own flavor of cloud storage, sometimes with their existing software products. Others focus on providing a new kind of back-end storage optimally designed for delivering cloud storage.
Roles[edit | edit source]
Provider[edit | edit source]
A cloud computing provider or cloud computing service provider owns and operates cloud computing systems to deliver service to other people. Usually this requires significant resources and expertise in building and managing the next generation of data centers. The companies listed in the Components section are providers.
User[edit | edit source]
A user is a consumer of cloud computing.
Vendor[edit | edit source]
A vendor sells products and services that facilitate the delivery, adoption and use of cloud computing. For example:
- Computer hardware (Dell, HP, IBM, Sun Microsystems)
- Computer storage (3PAR, EMC, MogileFS)
- Infrastructure (Solace Systems, Layer 7 Technologies, F5 Networks)
- Computer software (3tera, GigaSpaces, Hadoop)
Standards[edit | edit source]
A cloud standard is one of a number of existing (typically lightweight) open standards that have facilitated the growth of cloud computing, including:
- Application
- Client
- Infrastructure
- Platform
- Service
- Data (XML, JSON)
- Web Services (REST)
- Storage
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ The Internet Cloud
- ↑ Gartner Says Cloud Computing Will Be As Influential As E-business
- ↑ What's the difference Between Cloud Computing and SaaS?
- ↑ Distinguishing Cloud Computing from Utility Computing
- ↑ With Their Heads in the Clouds
- ↑ Microsoft Fueling Cloud Computing Initiatives
- ↑ http://www.informationweek.com/news/services/saas/showArticle.jhtml?articleID=207601148
- ↑ Cloud Computing: When Computers Really Do Rule
- ↑ What cloud computing really means
- ↑ July, 1993 meeting report from the IP over ATM working group of the IETF
- ↑ Internet Critic Takes on Microsoft
- ↑ Google and I.B.M. Join in ‘Cloud Computing’ Research
- ↑ Feature Guide: Amazon EC2 Availability Zones
- ↑ Building GrepTheWeb in the Cloud, Part 1: Cloud Architectures
- ↑ "Web Services Glossary". http://www.w3.org/TR/ws-gloss/.
- ↑ http://blogs.zdnet.com/igeneration/?p=500
- ↑ http://www.itpro.co.uk/606705/ballmer-microsoft-to-launch-cloud-os
- ↑ "About - What is the Azure Services Platform". Microsoft. http://www.microsoft.com/azure/whatisazure.mspx. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- ↑ Red Hat chief: 'The clouds will all run Linux'
- ↑ Lock-in, security loom as dark side of Compute Cloud
- ↑ LinuxWorld/Next Generation Data Center attendees get schooled in cloud computing
Other websites[edit | edit source]
- Chappell, David (August 2008). "A Short Introduction to Cloud Platforms" (PDF). David Chappell & Associates. Retrieved on 20 August 2008.
- Jones, M. Tim, Cloud Computing with Linux from IBM DeveloperWorks (2008-09-10).
- Kaye, Russell, Cloud Computing (QuickStudy) from ComputerWorld (2008-05-08).
- Martin & Hoover, Guide to Cloud Computing from InformationWeek (2008-07-21).
- Cloud Computing Community Wiki is a "new resource put together by several industry executives and bloggers".
- Cloud Computing Incidents Database (CCID) tracks and "provides historical data on cloud outages".
- What is Cloud Computing ? - Web 2.0 expo - A video where Tim O’Reilly, Dan Farber, Matt Mullenweg and others answer this question.
| Computer science Portal — All articles about computer science |